
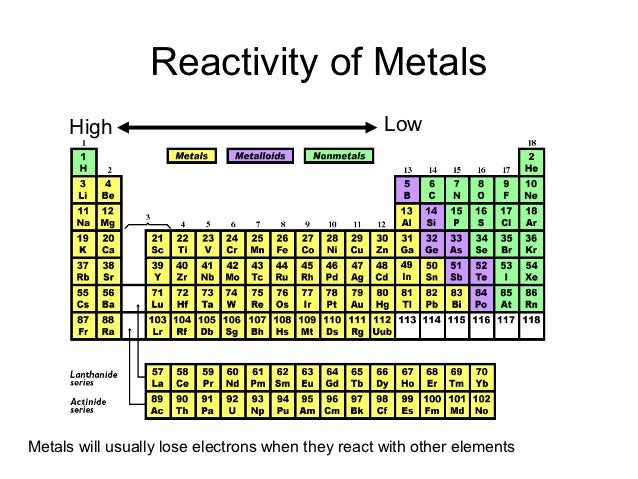
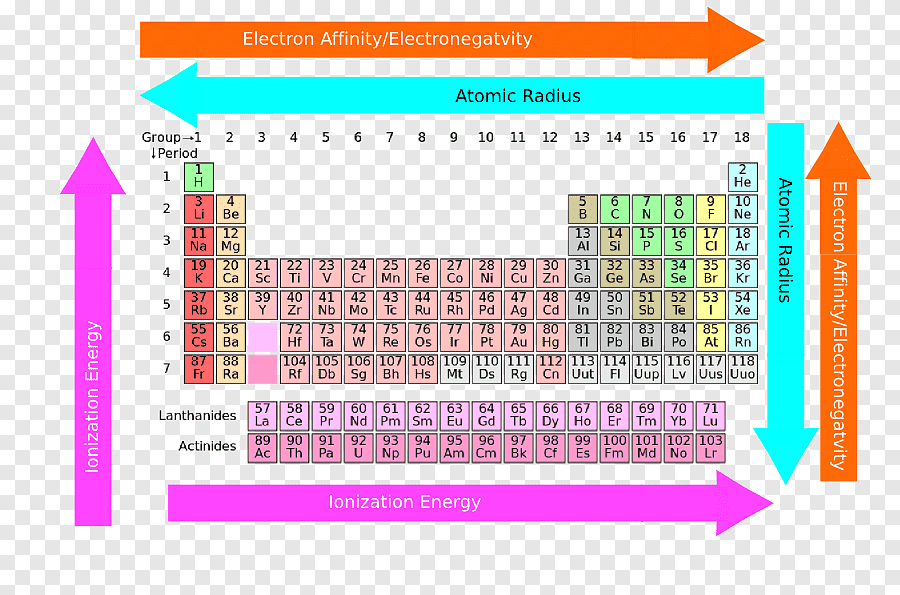
Hence, the hydroxides of these elements become more basic. As you move down the group, the reactivity decreases because the. Answer (1 of 2): Chemical Reactivity: METALS DOWN a Group: In METALS reactivity INCREASES as you go DOWN a Group because the farther down a Group of metals you go, the easier it is for electrons to be given or taken away, resulting in higher reactivity. As you go down the group, the reactivity.1 answer Top answer: a) Group 17 are the halogens, and they desire to gain an electron to complete the octet. Thus, the elements from the two extreme ends of the periodic table behave differently as expected.Īs we move down the group, the ionisation energy decreases and the electropositive character of elements increases. b) Group 1 are the alkali metals and they desire or tend to lose an electron to become stable. Conversely Cl 2O 7 gives strong acid called perchloric acid upon reaction with water So, it is an acidic oxide. Since sodium oxide reacts with water to give strong base sodium hydroxide, it is a basic oxide. Consider the reaction of alkali metals and halogens with oxygen to give the corresponding oxides. Let us analyse the nature of the compounds formed by elements from both sides of the periodic table. On the other hand the elements located in the top right portion have very high ionisation energy and are non-metallic in nature. The ionisation energy is directly related to the metallic character and the elements located in the lower left portion of the periodic table have less ionisation energy and therefore show metallic character. The noble gases having completely filled electronic configuration neither accept nor lose their electron readily and hence they are chemically inert in nature.
As a consequence of this, elements of these extreme ends show high reactivity when compared to the elements present in the middle. On the other hand, the elements on right side of the periodic table have high electron affinity and readily accept electrons. The elements on the left side of the periodic table have less ionisation energy and readily loose their valence electrons. The physical and chemical properties of elements depend on the valence shell electronic configuration as discussed earlier.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
